What Is Private Equity And How Does It Work: Best Guide 2021
Private equity funds are pools of capital to be purchased companies that represent a chance for a high rate of return. They include a set financial investment horizonRoi (ROI), typically ranging from 4 to 7 years, at which point the PE firm hopes to successfully leave the financial investment.
2. Buyout or Leveraged Buyout (LBO)Contrary to VC funds, leveraged buyout funds invest in more fully grown businesses, generally taking a controlling interest. The Bio of Tyler Tysdal LBOLeveraged Buyout (LBO) funds use comprehensive quantities of take advantage of to improve the rate of return. Buyout finds tend to be significantly bigger in size than VC funds. Exit Considerations, There are multiple consider play that affect the exit technique of a private equity fund.
Private Equity – Ares Management
In terms of a wholesale exit from the business, there can be a trade sale to another buyer, LBO by another private equity company, or a share repurchase. In terms of a partial exit, there could be a personal placement, where another investor purchases a piece of business. Another possibility is business restructuring, where external investors get included and increase their position in business by partially obtaining the private equity firm`s stake.
To keep learning and advancing your profession, the list below resources will be handy:.
A Note On Direct Investing In Private Equity – Caia Association
Looking into your family history with Ancestry!.?.!? PE-backed. But what exactly is private equity? A fundamental idea for anybody interested in finding out aboutor working in a market tangential tothe personal markets, this blog breaks down the basics of PE. What is private equity? Private equity (PE) is a kind of funding where cash, or capital, is invested into a business.

PE is a significant subset of a larger, more complicated piece of the monetary landscape referred to as the personal markets. Private equity is an alternative asset class together with real estate, venture capital, distressed securities and more. Alternative possession classes are considered less traditional equity investments, which means they are not as quickly accessed as stocks and bonds in the general public markets.
Types Of Private Equity Funds
What is a private equity fund? To buy a business, private equity investors raise liquidity pools of capital from minimal partners to form a fundalso called a private equity fund. Once they`ve struck their fundraising goal, they close the fund and invest that capital into appealing companies. Both private equity funds and hedge funds are limited to recognized financiers.
And shared funds are just allowed to gather management fees, whereas PE funds can gather efficiency charges, which is discussed more below. How do private equity companies make money? PE funds collect both management and performance fees. These can vary from fund to fund, however the. Determined as a percentage of properties under management or AUM, typically around 2%.
How Does A Private Equity Fund Work? Explaining Sponsors …
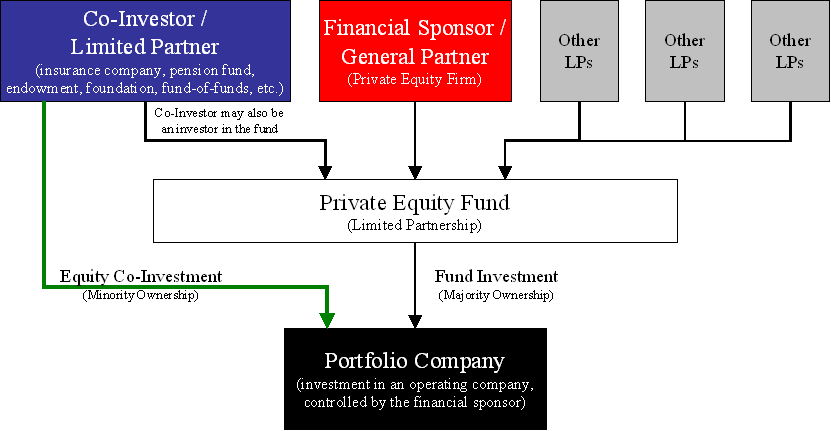

Determined as a portion of the benefit from investing, typically around 20%. These charges are planned to incentivize greater returns and are paid out to employees to reward their success. How does private equity work? To invest in a company, private equity financiers raise pools of capital from restricted partners to form the fund.
When a PE firm offers among its portfolio business to another business or investor, the company typically earns a profit and disperses go back to the limited partners that invested in its fund. Some private equity-backed business may likewise go public. What are some examples of private equity firms? The Blackstone Group Headquartered in New York City, the investment company purchases PE, real estate and more.
Private Equity – Ares Management
So, VC is a form of private equity. Here are some extra differences between PE and VC. Private equity PE companies often buy fully grown businesses in standard markets. Using capital dedicated from LPs, PE investors invest in appealing companiestypically taking a bulk stake (> 50%). When a PE firm sells among its portfolio companies to another business or financier, returns are distributed to the PE financiers and to the LPs.
Equity capital VC firms typically purchase tech-focused start-ups and other young companies in their seed. Utilizing dedicated capital, VC financiers usually take a minority stake